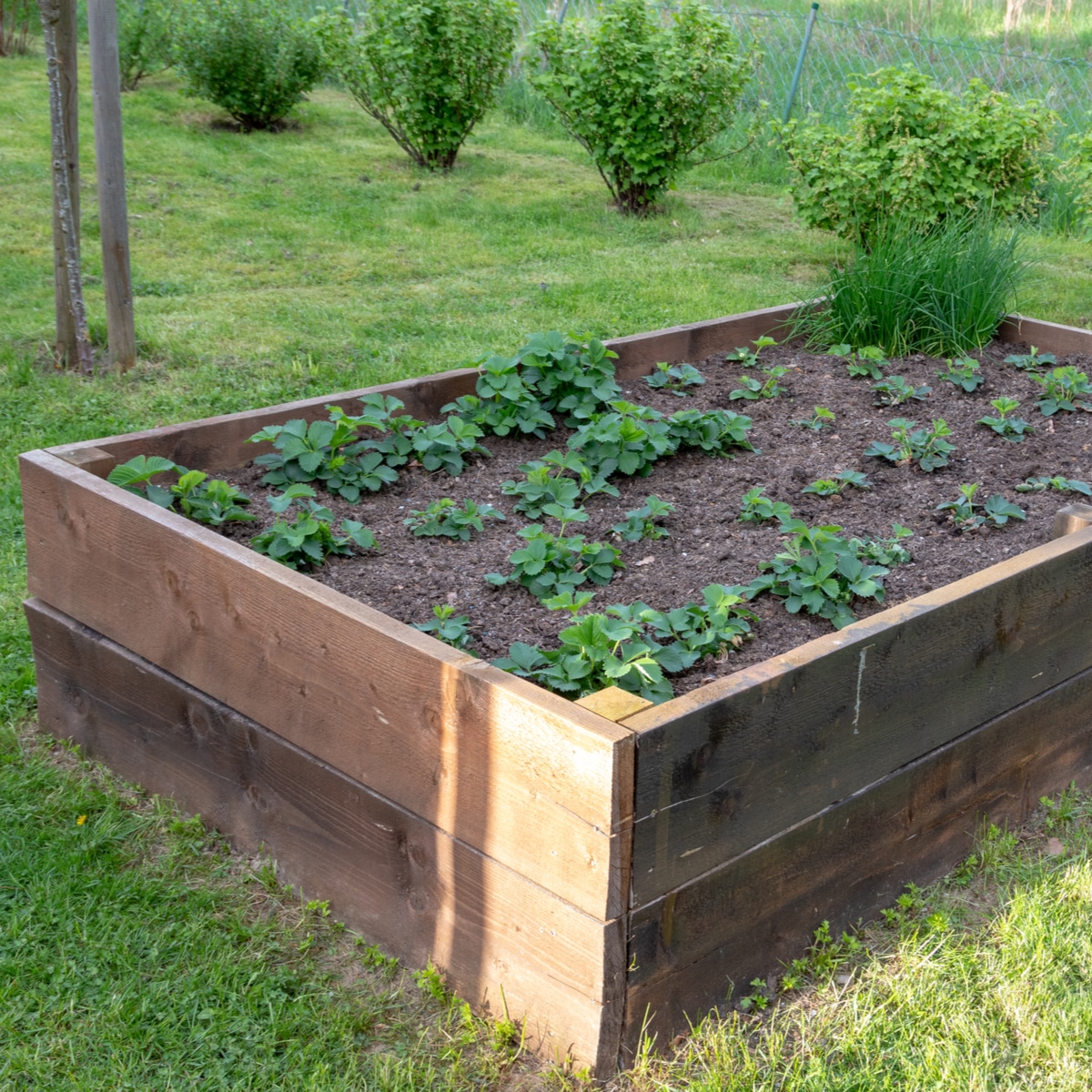
Methyl Iodide is used with strawberry plants as a soil fumigant to control soil-borne pests and diseases, improve crop yields, and increase production. Before planting strawberries, methyl iodide is injected into the soil, targeting unwanted pests and fungi that could lead to plant diseases.
Using methyl iodide in California supports crop yields for the world’s biggest strawberry-growing region. While concerns have been raised by environmentalists and some growers about the safety of methyl iodide, many believe that its benefits outweigh the risks when used properly.
The debate over the use of methyl iodide with strawberry plants highlights the importance of finding sustainable solutions for agriculture that not only protect our food but also the environment.
What Is Methyl Iodide?
Methyl iodide is a fumigant used with strawberry plants to eliminate soil-dwelling fungi and bacteria that can cause plant diseases. It is also used as an intermediate in the manufacture of some pharmaceuticals and pesticides.
Methyl iodide is a colorless liquid that is commonly used as a soil fumigant for strawberry plants. It is a highly reactive compound that has a strong odor and is easily absorbed into the soil. Methyl iodide is used as an alternative to methyl bromide, another fumigant that is no longer in use due to its harmful environmental effects. The use of methyl iodide has been controversial due to concerns over its potential health hazards. Despite this, methyl iodide has proven to be an effective pesticide, with its usage widely accepted in many agricultural industries. It is also used in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals and as an intermediate in various chemical processes. In microscopy, it is used to prepare tissue samples for examination under a microscope.
Credit: calag.ucanr.edu
Why Use Methyl Iodide With Strawberry Plants?
Methyl iodide is commonly used as a soil fumigant for strawberry plants, as it effectively controls soil-borne pests and diseases. Its usage allows for increased yields and better quality strawberries.
Methyl iodide is used as an effective replacement for methyl bromide in fumigating soil to control soil-borne pathogens on strawberries. Methyl bromide has been banned due to its harmful effects on the environment and human health. Methyl iodide has been found to be a better alternative, as it has a lower impact on the ozone layer and is less toxic. Its benefits on strawberry plants include improved yield, longer shelf life, and better fruit quality. Despite some concerns raised by strawberry growers over its safety, methyl iodide has been approved by regulatory agencies for use in agriculture.Methyl Iodide Vs Methyl Bromide
Methyl iodide is used as a replacement for methyl bromide in soil fumigation for strawberry plants. It helps to control diseases and pests in the soil while remaining environmentally friendly and safe for human consumption.
Methyl iodide and Methyl bromide are both fumigants used to control fungi and pathogens in soil before planting crops. However, Methyl iodide is a better alternative to Methyl bromide due to several benefits. Methyl iodide has a lower potential to deplete the ozone layer, lower toxicity to humans and the environment, and it is more effective in killing soil-borne pests. Methyl iodide is also more versatile as it can eliminate pests in different types of soil and plant species. As a result, many organic strawberry farmers are turning to Methyl iodide instead of Methyl bromide to ensure the safety and quality of their crops and the environment.Controversies Surrounding Methyl Iodide
The use of methyl iodide with strawberry plants has caused controversy due to its potential health and environmental risks. Strawberry growers have relied on fumigants like methyl bromide to treat soil-dwelling fungi, but the phase-out of methyl bromide has led to the consideration of alternatives like methyl iodide.
Methyl iodide is a fumigant that is used in agriculture to control soil waterborne pests and diseases. However, its use has raised environmental concerns due to its potential to harm non-target organisms and groundwater contamination. It has also been linked to health risks and is a highly toxic substance that can cause damage to the lungs and nervous system. Despite these controversies, some farmers continue to use it as an alternative to methyl bromide, which has been banned due to its effects on the environment. Proper handling and precautions should be taken when using methyl iodide to ensure the safety of workers and the environment.Alternatives To Methyl Iodide And Methyl Bromide
Methyl iodide and methyl bromide have been widely used as fumigants to treat soil when growing strawberries, but due to their toxicity, alternatives are being sought. Organic farming methods rely on crop rotation, steam or heat treatment, and other natural soil amendments to manage pests and diseases. Crop rotation and cover crops maintain soil health and reduce the risk of pests and diseases by interrupting their life cycles. Steam or heat treatment of soil can also kill pathogens, fungi, and weeds. However, these methods require careful planning and may not be suitable for all farms. While methyl iodide is sometimes used as an intermediate in manufacturing pharmaceuticals and pesticides, it is highly toxic and has been linked to cancer and other health issues. Instead, organic farmers use natural methods to promote healthy soil and crops. By using sustainable practices, farmers can reduce the need for harmful fumigants and promote a healthier environment for workers and consumers. |

Credit: www.mcgill.ca
Credit: strawberryplants.org
Frequently Asked Questions For Why Use Methyl Iodide With Strawberry Plants?
What Is The Use Of Methyl Iodide?
Methyl iodide is used as an intermediate in the production of pesticides and pharmaceuticals. It is also used in methylation processes and in microscopy.
Is Methyl Bromide Used On Strawberries?
To raise perfect berries, growers often use methyl bromide as a fumigant to eliminate soil-dwelling fungi and bacteria that can cause diseases to plant. There is no indication that methyl bromide is used directly on strawberries, but in the soil, a few weeks before planting.
Methyl iodide, another soil fumigant, was developed to replace methyl bromide. Strawberry growers used to rely on methyl bromide.
What Chemicals Are Used On Strawberries?
Methyl iodide is used as a soil fumigant for strawberries, to control fungi and bacteria that cause plant diseases. It is registered as a replacement for methyl bromide, a favored fumigant in California, which is being phased out due to compliance with the Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer.
Why Do Strawberries Have So Much Dna?
Strawberries have a high amount of DNA because they are octoploid, meaning they have eight sets of chromosomes in each cell. This makes them an ideal fruit for DNA extraction labs as they yield more DNA compared to other fruits like bananas and kiwis.
Conclusion
Methyl iodide has proven to be a valuable tool for strawberry growers, as it effectively controls soil-borne pests and diseases, resulting in increased crop yields. While there have been concerns regarding its safety and environmental impact, studies have shown that its use can be managed safely.
Ultimately, the decision to use methyl iodide should be made in consultation with experts and based on the specific needs of each farm. By incorporating this fumigant into their farming practices, growers can support the production of high-quality, flavorful strawberries for consumers around the world.

I am a graduate of Bangladesh Agricultural University, where I delved into various agricultural disciplines, equipping me with a profound understanding of agriculture. Beyond academics, I have hands-on experience in gardening and crop cultivation. My passion is to embrace sustainable farming and horticulture. With a BSc in Agriculture, I am dedicated to promoting environmentally conscious and efficient agrarian practices.
Bachelor of Science (BSc) in Agriculture (Hons.)
Master of Science. (Sustainable Agriculture & Food Security ) (MS)
Bangladesh Agricultural University



