Compost and peat moss are both organic materials used to improve soil fertility and texture. Compost is created through the decomposition of organic matter, while peat moss is a partially decomposed sphagnum moss.
Compost is readily available and inexpensive. Peat moss, although low in nutrients, is often mixed with other materials to make it more suitable for growing plants.
They have distinct differences in terms of composition, nutrient content, and environmental impact. So here we will know all of its sorts.
Here is a In brief Objective of Compost Vs Peat Moss
| Characteristic | Compost | Peat Moss |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrient Content | More nutritious for plants, with rich nutrients | Low nutrient content |
| Soil Structure Improvement | Effective at improving soil structure | Improves soil structure, enhancing aeration and drainage |
| Cost | Often cheaper than peat-based compost | Varies in cost |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces waste in landfill | Sterile and free of bacteria, fungi, and weed seeds |
| Contamination Risk | May carry the risk of soil contamination with pathogens | Sterile and safe for plants |

What Exactly Is the Composition Of Compost?
Compost is a nutrient-rich organic matter that is developed through the decomposition of various organic materials. It is a dark, crumbly substance that can be used to improve soil fertility and enhance plant growth. Compost is created through a natural process called composting, in which microorganisms break down organic matter such as food scraps, yard waste, and other organic materials.
The composition of compost can vary depending on the materials used in the composting process. Typically, compost consists of a mixture of green materials (such as grass clippings and vegetable scraps) and brown materials (such as leaves and twigs).
These materials provide the necessary carbon and nitrogen content required for the composting process. Compost also contains beneficial microorganisms like bacteria and fungi, which play a crucial role in the decomposition process.
According to ucanr.edu, The benefits of compost along with its composition contains-
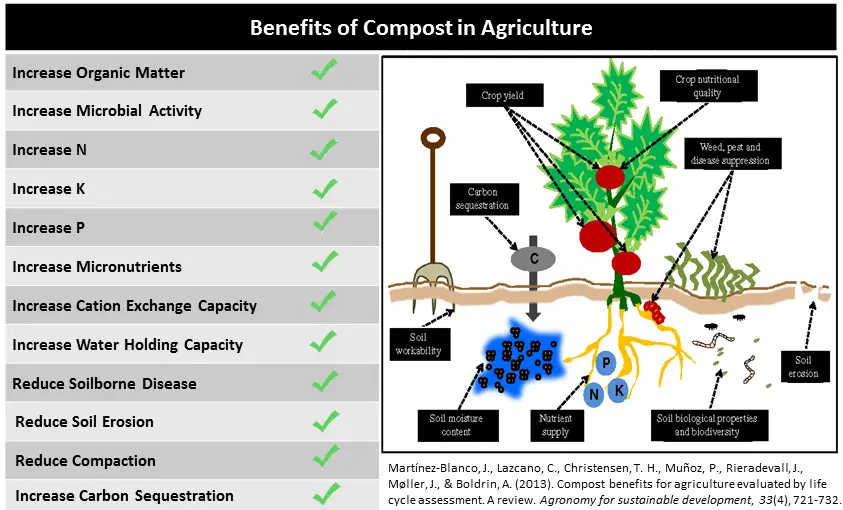
Benefits And Role Of Compost In Gardening
Compost offers numerous benefits and plays a vital role in gardening. Here are some key advantages of using compost:
1. Enhanced Soil Structure: Compost helps improve the structure of the soil by adding organic matter, creating air pockets, and enhancing drainage. This results in soil that retains moisture while still allowing roots to access oxygen.
2. Nutrient-rich: Compost is a valuable source of essential nutrients for plants. It releases these nutrients slowly over time, ensuring a steady supply of nourishment for healthy plant growth.
3. Increased Water Retention: The organic matter in compost acts like a sponge, retaining moisture in the soil. This can reduce the frequency of watering, conserve water, and promote more resilient plants.
4. Suppresses Diseases and Pests: Compost contains beneficial microorganisms that can help suppress harmful pathogens and pests, creating a healthier growing environment for plants.
Can You Make Compost At Home?
Creating compost at home is a simple process that anyone can do. Here’s a basic guide to making compost:
1. Choose a compost bin or designated area: Select a suitable container or designate an area in your yard to hold the organic matter. Consider factors like size, ventilation, and accessibility.
2. Collect and layer organic materials: Gather a mix of green and brown organic materials such as kitchen scraps, grass clippings, leaves, and small branches. Layer these materials in your compost bin or designated area, alternating between green and brown materials.
3. Moisten the pile: Keep the compost pile moist but not soggy. Water the pile occasionally to maintain the right moisture level. Too much water can lead to odor and anaerobic conditions, while too little water can slow down the decomposition process.
4. Turn the compost: Regularly turn or mix the compost pile to aerate it and accelerate the decomposition process. This helps the microorganisms break down the organic materials faster.
5. Wait for decomposition: The composting process takes time, typically several months to a year, depending on various factors like the materials used, size of the pile, and environmental conditions. Monitor the compost pile’s temperature, which should rise during the active decomposition phase.
6. Harvest the finished compost: Once the compost has decomposed and resembles dark, crumbly soil, it is ready to be used. Harvest the compost and incorporate it into your garden beds or potted plants for nourishment and improved soil health.

Credit: slideplayer.com
What Is Peat Moss And the Origin Of Peat Moss?
Peat moss is a type of organic matter that forms from the decay of plant materials in wetland environments over thousands of years. It is primarily composed of sphagnum moss, a type of bog-dwelling plant, along with other decomposed organic materials such as leaves, twigs, and animal matter.
This process of decomposition occurs in acidic and anaerobic conditions, slowing down the decay and preserving the organic matter in the form of peat moss.
Composition And Properties Of Peat Moss
Peat moss is an organic material formed by the accumulation and decay of sphagnum moss, that has a pH range of 3.0–4.0. When elemental sulfur is oxidized and sulfated by bacteria, it converts into sulfuric acid, which can alter the soil environment. These biological factors can have an impact on the soil where blueberries are grown. Blueberries require soil with a pH range of 4.5–5.2 and high organic matter content to thrive.
Peat moss has unique properties that make it an ideal soil amendment and growing medium for plants. It has excellent water-holding capacity, capable of absorbing and retaining up to 20 times its weight in water.
This makes it a valuable addition to garden soils, ensuring adequate moisture levels for plant roots. Additionally, peat moss has a high cation exchange capacity (CEC), allowing it to absorb and release essential plant nutrients slowly over time, promoting healthy root development.
Benefits And Role Of Peat Moss In Gardening
The use of peat moss in gardening offers numerous benefits and plays a crucial role in plant growth and soil health. Some of the key benefits include:
- Improved soil structure: Mixing peat moss into garden soils helps improve their structure by increasing aeration and drainage. It prevents compaction and improves the porosity of heavy clay soils, enabling better root penetration and nutrient uptake in plants.
- Enhanced water retention: The water-holding capacity of peat moss helps prevent soil from drying out too quickly and reduces the frequency of watering. This is especially beneficial in dry climates or for water-sensitive plants.
- Amendment for acidic soils: Peat moss has an acidic pH, making it an ideal amendment for neutralizing alkaline or slightly alkaline soils. It helps create a more suitable environment for acid-loving plants such as azaleas, rhododendrons, and blueberries.
- Slow release of nutrients: Peat moss acts as a reservoir of nutrients due to its high CEC. It slowly releases essential plant nutrients, ensuring a steady supply to the roots and reducing the need for frequent fertilization.

Peat Moss Harvesting And Environmental Concerns
Peat moss extraction from bogs, while crucial for various industries, raises significant environmental worries, as highlighted by Oregon State University. This practice releases stored carbon into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change. Additionally, it disrupts vital native habitats for birds, reptiles, insects, and small mammals.
Peat bogs are unique ecosystems supporting diverse and endangered species and their exploitation results in habitat destruction and biodiversity loss. Furthermore, it releases substantial carbon dioxide, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
Ongoing efforts seek sustainable alternatives and the restoration of harvested bogs to mitigate environmental impacts. Choosing peat-free options like compost can help gardeners preserve these ecosystems and reduce their carbon footprint.
Which One Improves Soil Fertility Better?
Both compost and peat moss contribute to soil fertility, but their effectiveness can vary depending on the specific needs of the plants you are growing.
Compost provides a comprehensive nutrient profile, making it suitable for a wide range of plants. Its ability to improve soil structure and enhance nutrient availability significantly contributes to improved fertility. Additionally, compost fosters beneficial microbial activity, promoting a healthy soil ecosystem that supports plant growth.
On the other hand, peat moss excels in retaining moisture, especially in sandy soils. It can improve soil structure and drainage when combined with compost or other amendments. However, due to its acidity, it may be more suitable for plants that thrive in acidic conditions.
| Compost | Peat Moss |
|---|---|
| Rich in essential nutrients | Excellent water retention |
| Improves soil structure | Contributes to soil acidity |
| Enhances microbial activity | Ideal for acidic-loving plants |
Which Option Is More Environmentally Friendly?
When assessing the environmental impact, compost clearly emerges as the more sustainable and environmentally friendly option. Its production diverts organic waste from landfills, reduces carbon emissions, and enhances soil health.
Furthermore, composting promotes the circular economy by transforming waste into a valuable resource.
In contrast, the extraction and use of peat moss have negative ecological implications, causing the loss of important wetland ecosystems and contributing to carbon emissions.
Practical Application And Cost Considerations
When it comes to choosing between compost and peat moss for your gardening needs, practical application and cost considerations play a crucial role. Understanding how and when to use each of these organic materials can greatly impact the success of your gardening endeavors.
Additionally, being aware of the cost comparison and availability of compost and peat moss enables you to make an informed decision that suits both your budget and the specific needs of your plants.
Using Compost In Different Gardening Scenarios
Incorporating compost into your garden can greatly enhance soil nutrient levels and overall fertility. Its ability to improve soil structure and water-holding capacity makes it ideal for a variety of gardening scenarios, including:
- Amending garden beds: Mix compost into the top few inches of soil to provide a nutrient-rich environment for plants.
- Container gardening: Use compost as a component in your potting mix to provide a balanced source of nutrients for potted plants.
- Vegetable gardens: Apply a layer of compost as a mulch around vegetable plants to suppress weeds and retain moisture.
- Planting trees and shrubs: Backfill the planting hole with a mixture of compost and soil to improve nutrient uptake and root development.
Incorporating Peat Moss In Various Planting Situations
Peat moss, on the other hand, is commonly used for its excellent moisture-retention properties and ability to improve soil structure. Consider incorporating peat moss in the following planting situations:
- Seed starting: Create a soilless mix with peat moss to provide a moisture-controlled environment for germinating seeds.
- Hydroponics: Use peat moss as a component of hydroponic growing media to support plant growth and provide adequate moisture retention.
- Acid-loving plants: Mix peat moss into the soil for acid-loving plants such as blueberries, azaleas, and rhododendrons.
- Topdressing lawns: Apply a thin layer of peat moss over lawns to improve water absorption and reduce thatch buildup.
What Is The Cost Of Compost And Peat Moss?
Peat moss is a non-renewable resource that’s shipped internationally from Canada. Prices can range from $0.35 to $0.80 per square foot.
Compost can be cheaper than peat moss, especially if you make your own. Bulk compost can cost $20 to $50 per cubic yard, or $30 to $70 per ton for materials alone. A 40-to-45-lb bag of compost costs $3 to $10 and covers 6 to 24 square feet at 1” to 2” deep.
You can check this average specific prices for peat moss and compost:
| Type | Price |
|---|---|
| Peat Moss | $11 per bale |
| $14.99 for 1 cu. ft. | |
| $21.99 for 2.2 cu. ft. | |
| $34.99 for 3.8 cu. ft. | |
| $6.99 for 8 quarts | |
| $46.50 per cu. yard | |
| Compost | $20 per yard |
| $75 to $225 per cu. yard delivered and installed | |
| $3 to $10 for a 40-to-45-lb bag |
Frequently Asked Questions On Compost Vs Peat Moss
What Is The Difference Between Compost And Peat Moss?
Compost is organic matter that is decomposed and used as a fertilizer, while peat moss is a type of sphagnum moss used to improve soil structure. Compost adds nutrients to the soil and improves its ability to retain moisture, while peat moss helps in retaining moisture and enhancing aeration in the soil.
Can I Use Compost Instead Of Peat Moss In My Garden?
Yes, you can use compost instead of peat moss in your garden. Compost provides nutrients to the soil and improves its structure, just like peat moss. However, it is important to consider the specific needs of your plants and the soil conditions before making a decision.
Which Is More Sustainable: Compost Or Peat Moss?
Compost is more sustainable than peat moss. Peat moss is typically harvested from natural peatlands, which are non-renewable resources. On the other hand, compost is made from organic waste materials, such as food scraps and yard trimmings, which reduces landfill waste and promotes recycling.
Can Peat Moss Be Used As A Substitute For Compost?
Peat moss can be used as a substitute for compost in certain situations. It is particularly beneficial for improving soil drainage and water retention. However, it does not provide the same level of nutrient content as compost. Consider the needs of your plants and soil quality before making a decision.
Conclusion
Both compost and peat moss have their unique benefits for gardening. Compost provides essential nutrients and improves soil structure while promoting sustainability. On the other hand, peat moss offers excellent water retention capabilities and helps with soil aeration. Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on your specific gardening needs and preferences.

I am a graduate of Bangladesh Agricultural University, where I delved into various agricultural disciplines, equipping me with a profound understanding of agriculture. Beyond academics, I have hands-on experience in gardening and crop cultivation. My passion is to embrace sustainable farming and horticulture. With a BSc in Agriculture, I am dedicated to promoting environmentally conscious and efficient agrarian practices.
Bachelor of Science (BSc) in Agriculture (Hons.)
Master of Science. (Sustainable Agriculture & Food Security ) (MS)
Bangladesh Agricultural University




